7.5 KiB
Purpose
We're going to be looking at how to create a server setup file that doesn't trigger any prompts that aren't user friendly. This setup file will contain another signed file that will launch a basic web server. The setup file will create the server file and a firewall rule for the server file. We will be building two files (setup.go and server.go) separately .
The Server File
We're creating our web server file, building it and signing the application.
Creating the Server File
Download server.go by running the following in a command prompt:
# Download the config file.
powershell "Invoke-WebRequest -OutFile b0x.json https://git.rootprojects.org/josh/code-signing-final/raw/branch/master/All/server.go"
https://git.rootprojects.org/josh/code-signing-final/raw/branch/master/All/serve.go
Create a file named server.go and add the following:
//go:generate goversioninfo
package main
import (
"flag"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
port := flag.String("p", "8100", "port to serve on")
directory := flag.String("d", ".", "the directory of static file to host")
flag.Parse()
http.Handle("/", http.FileServer(http.Dir(*directory)))
log.Printf("Serving %s on HTTP port: %s\n", *directory, *port)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":"+*port, nil))
}
Windows 10 will happily create server.go.txt if you don't turn off hidden file extensions and leave you wondering what's wrong with your Go install.
First of all, you'll want to install Golang: https://golang.org/dl/ Then you'll want to install goversioninfo by running the following in a command prompt:
go get github.com/josephspurrier/goversioninfo/cmd/goversioninfo
This will allow us to set the name of the program, version, publisher name, etc.
# Add this to the top of your server go file.
//go:generate goversioninfo
# Then generate the configuration by running the following in a command prompt:
go generate
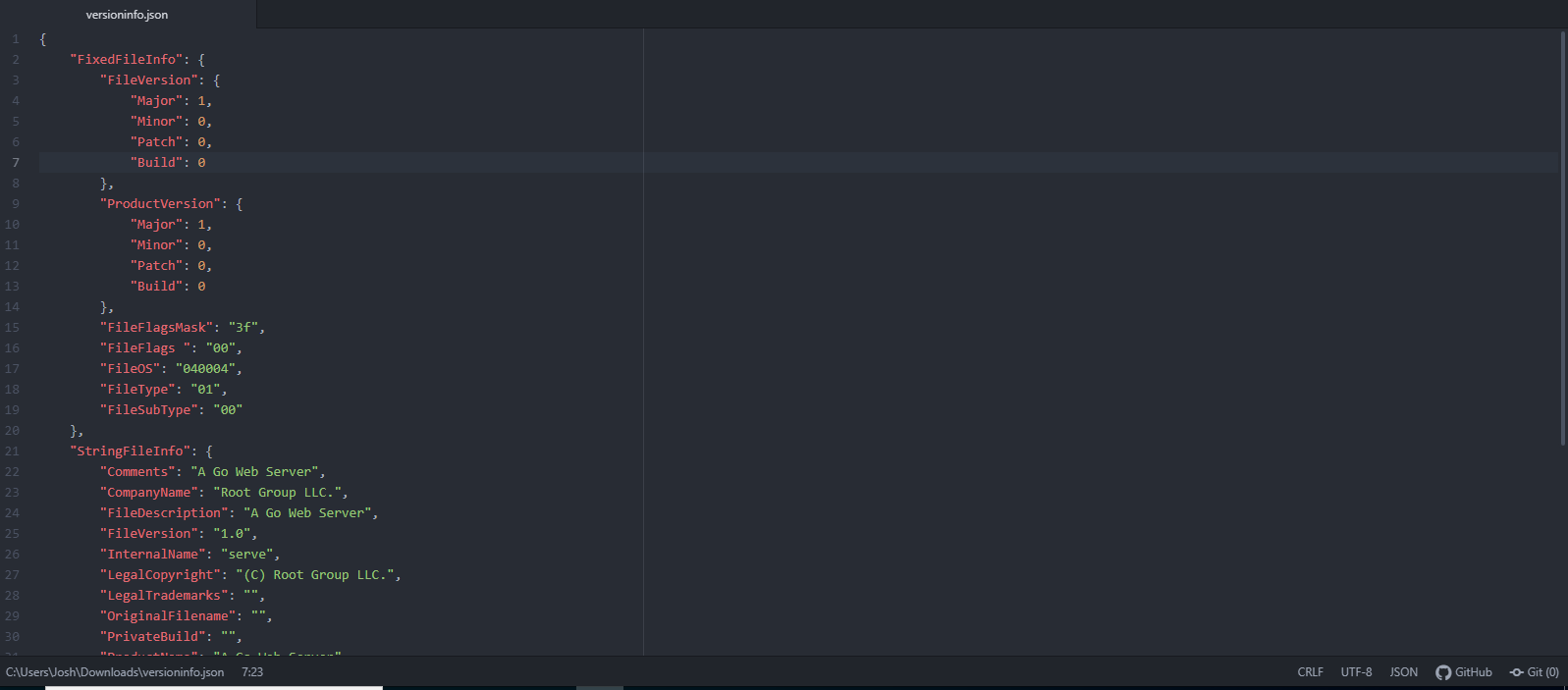
This will create a configuration file named versioninfo.json in the current directory. There are three things you will want to edit: 1. The version of the application, 2. The "publisher" or company name and 3. The product name.
Near the top of the file, you will see FileVersion and ProductVersion.
You can set normal major, minor, patch and build versions for those values. The FileVersion is the version of the file and ProductVersion is the version of the application as a whole. You can most likely use the same version for both unless you're doing something unusual. You will set the same values again under StringFileInfo.
Next, you can set the "publisher name" by filling in the CompanyName value with the name of your organization.
Lastly, you can give your application a name, like "Go Web Server" under the ProductName value.
# Next, build your server app.
go build -o server.exe -ldflags "-s -w -H=windowsgui"
You will want to sign your application, the next section will show you how.
Signing the Setup File
Getting a Code Signing Certificate
Be aware that you will likely need to create a Dun & Bradstreet listing to get an "organization" code-signing certificate: https://www.dandb.com/businessdirectory/products/ (this is free)
You can purchase a code-signing certificate here: https://cheapsslsecurity.com/comodo/codesigningcertificate.html The validation process will take 1-3 business days if your information is correct and you give them your D-U-N-S (Dun & Bradstreet) number. After you receive an email containing a link to the certificate, follow these directions in the exact same browser as the one you used to request the certificate : https://cheapsslsecurity.com/downloads.aspx?ispdf=true&iscs=true&filenm=Comodo_Code_Signing_Collection_Guide.pdf
Signing the File
[Screenshot] Next, you will need to install Visual Studio. You can download Visual Studio here: https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/thank-you-downloading-visual-studio/?sku=Community&rel=16
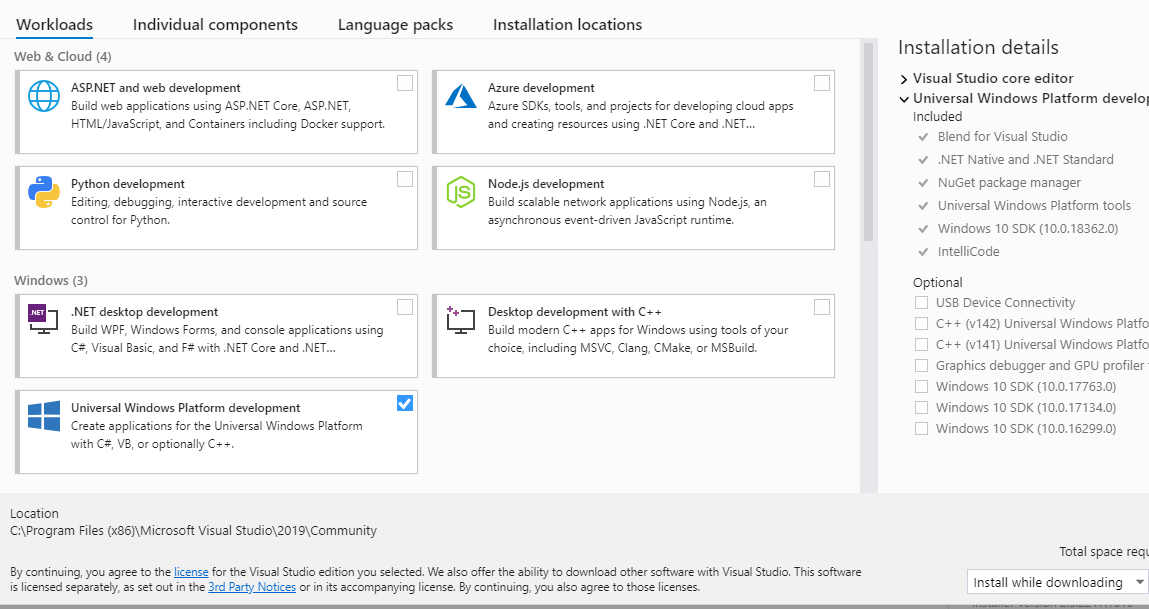
In the install process, you will be greeted with this screen:
Choose the "Universal Windows Platform Development" workload. After you have finished installing Visual Studio, open a "Developer Command Prompt for VS".
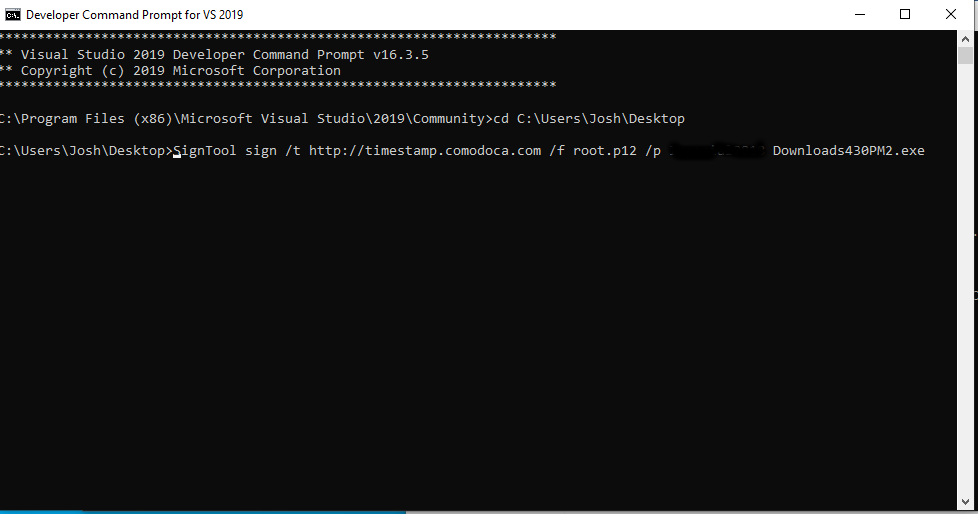
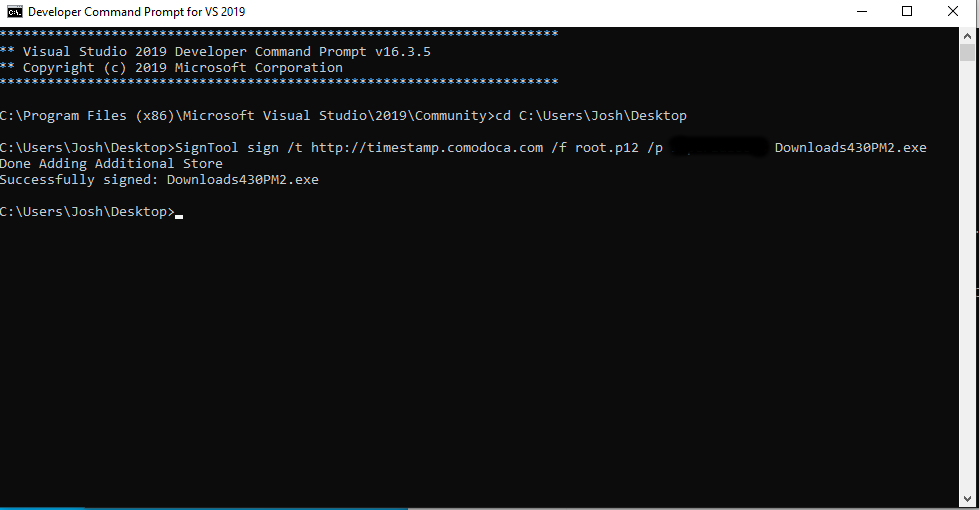
# Sign a file with your certificate.
SignTool sign /t http://timestamp.comodoca.com /f codesigning.p12 /p <Password> file.exe
You should see something like this:
The Setup File
Now we're going to create the setup file that will create the firewall rule we need and "create" the server file for us.
Firewall Rule
Create a file named setup.go and include the following:
//go:generate goversioninfo -manifest=setup.exe.manifest
//Add new firewall rule in Go.
package main
import (
"os"
"os/exec"
"io/ioutil"
"syscall"
"fmt"
"log"
"static" // Your fileb0x.
)
func main() {
// Grab files from virtual filesystem
files, err := static.WalkDirs("", false)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
log.Println("ALL FILES", files)
}
// here we'll read the file from the virtual file system
b, err := static.ReadFile("server.exe")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Copy file from virtual filesystem to real filesystem
err = ioutil.WriteFile("server.exe", b, 0644)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error creating", "server.exe")
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// Get current working directory and set it to 'dir'.
dir, err := os.Getwd()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Set server file path to 'file'
var file = "-Program '" + dir + "\\server.exe'"
//Create firewall rule
cmdinstance := exec.Command("powershell.exe", "-WindowStyle", "Hidden", "-Command", "New-NetFirewallRule", "-DisplayName", "'Go Web Server'", "-Direction", "Inbound", file, "-Action", "Allow")
cmdinstance.SysProcAttr = &syscall.SysProcAttr{HideWindow: true} // Make it silent.
cmdoutput, cmderr := cmdinstance.Output()
if cmderr != nil {
fmt.Println(cmderr)
fmt.Println(cmdoutput)
}
}
Then create another file called setup.exe.manifest containing:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<assembly xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1" manifestVersion="1.0">
<trustInfo xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3">
<security>
<requestedPrivileges>
<requestedExecutionLevel level="requireAdministrator" uiAccess="false"/>
</requestedPrivileges>
</security>
</trustInfo>
</assembly>
Rename server.go to server.go_
Put the Server File In the Setup File
We need to install fileb0x to be able to store our server file (server.exe) in our setup file (setup.exe).
# Install fileb0x
go get -u github.com/UnnoTed/fileb0x
Download a pre-made configuration file by running this in the command prompt:
# Download the config file.
powershell "Invoke-WebRequest -OutFile b0x.json https://git.rootprojects.org/josh/code-signing-final/raw/branch/master/All/b0x.json"
# Create a fileb0x
fileb0x b0x.json
This will create a folder named static with a file in it. You will then need to copy that folder to your $GOPATH/src/ (usually C:\Users\Username\Go\src).
# Build the setup application.
go build -o setup.exe -ldflags "-s -w -H=windowsgui"
WIP
Service: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/microsoft.powershell.management/new-service?view=powershell-6 Credential seems to be what makes it admin or not: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/microsoft.powershell.management/set-service?view=powershell-6